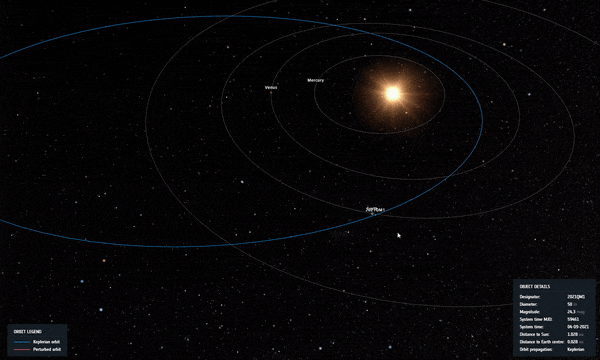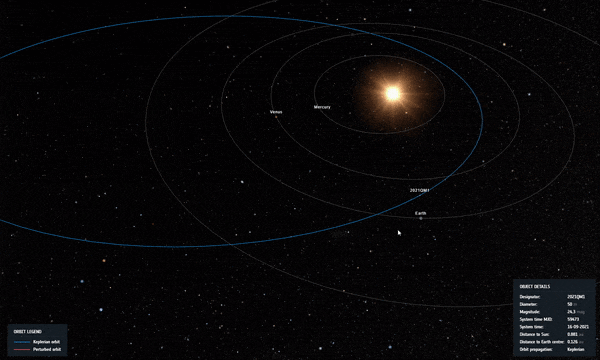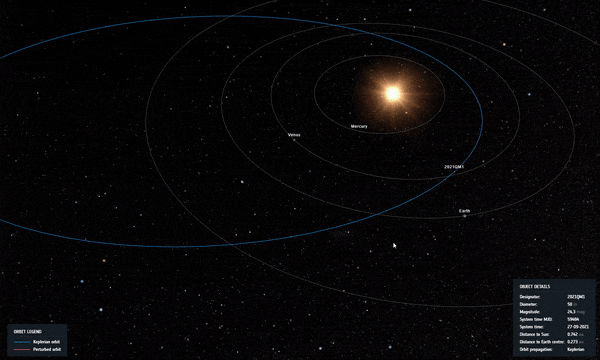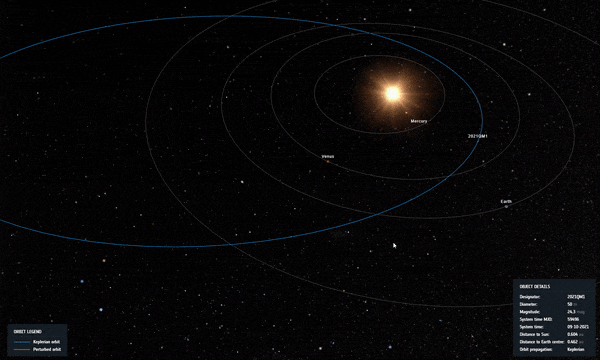
تمت إزالة الكويكب “2021 QM1” رسميًا من قائمة مخاطر الكويكبات التابعة لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية. لا يزال هناك 1،377 كويكب. (وجهة نظر الفنان لكويكب يدور حول الأرض.)
وكالة الفضاء الأوروبية (ESA) ترفض الاصطدام في عام 2052 لأنها تحسب يوم الكويكب
في الوقت المناسب تمامًا لليوم العالمي للكويكب: مع الاحتمال الحقيقي لضرب الأرض في 2 أبريل 2052 ، استمرت صخرة الفضاء المهددة لعدة أشهر في قائمة المخاطر العالمية. حاليًا ، يعمل فريق الكويكبات التابع لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية مع خبراء أوروبيين من جنوب أوروبا. مراقب ([{” attribute=””>ESO) has officially removed ‘2021 QM1’ from their asteroid risk list, a result of skilled observations and analysis of the faintest asteroid ever observed with one of the most sensitive telescopes ever constructed.
With Asteroid Day Live 2022 set for June 30, we can safely say that the riskiest asteroid known to humankind in the last year will not impact the Earth – at least not for the next century.
What was it like to track this asteroid? Get the full story in ESA’s fascinating behind-the-scenes look at how European experts handle asteroid risks in the official countdown to Asteroid Day live on June 30, airing at 10:25 CEST on AsteroidDay.org and via ESA WebTV.

Asteroid 2021 QM1, once thought to have a chance of impacting Earth in 2052, was spotted passing through a region of the sky with the Milky Way just behind it. The small, faint, receding asteroid had to be found against a backdrop of thousands of stars, with red crosses indicating the path of the object. Credit: ESO/O. Hainaut
Impact 2052
2021 QM1 was first discovered on August 28, 2021, by the Mount Lemmon Observatory, located north of Tucson, Arizona. At the beginning, nothing stood out as unusual about the discovery – about a dozen new near-Earth asteroids are identified every dark night. Routine follow-up observations were subsequently acquired from telescopes around the globe, but these began to tell a more worrying story.
“These early observations gave us more information about the asteroid’s path, which we then projected into the future,” said Richard Moissl, ESA’s Head of Planetary Defense.
“We could see its future paths around the Sun, and in 2052 it could come dangerously close to Earth. The more the asteroid was observed, the greater that risk became.”
https://www.youtube.com/watch؟v=crrRHTuPCfc
من المهم ملاحظة أن الحسابات المدارية تخضع لبعض عدم اليقين بناءً على عدد قليل من الملاحظات الليلية ، ولهذا السبب ستتم إضافة الكويكبات إلى قائمة مخاطر وكالة الفضاء الأوروبية بمجرد اكتشافها ، ثم إزالتها بمجرد جمع البيانات ، والكويكب ثبت أنه آمن. في هذه الحالة ، هذا غير ممكن.
المحاذاة الكونية المؤسفة
مع ازدياد الخطر على ما يبدو ، حدثت محاذاة كونية مثالية: لقد جعل مدار الكويكب من الأرض أقرب إلى الشمس ، وظل غير مرئي لعدة أشهر بسبب الوهج الرائع لنجمنا.
أوضح ماركو ميتشيلي ، عالم الفلك في مركز تنسيق المواد (NEOCC) التابع لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية: “كان علينا الانتظار”.
“ولكن للتغطية على الأشياء ، نعلم أن 2021 QM1 تبتعد عن الأرض في مدارها الحالي – مما يعني أنه عند وهج الشمس ، يمكن أن تشعر بالدوار بشكل لا يمكن اكتشافه.”
بينما كانوا ينتظرون ، استعدوا.
أولوية الوصول إلى أحد أقوى التلسكوبات على الأرض
المختبر الأوروبي الجنوبي تلسكوب أكبر (VLT) كانت أساسية وجاهزة. بمجرد أن يبتعد الكويكب البالغ ارتفاعه 50 مترًا عن ضوء الشمس – ويسمح الطقس بذلك – سيحقن VLT الخاص بـ ESO زجاجه البالغ 8 أمتار في الصخور المختفية.

أكبر تلسكوب ESO (VLT) ، القمر الدرامي خلف تشيلي. عندما يغرب البدر ، تكون الشمس على وشك أن تشرق في الأفق المعاكس. لقد أغلق التلسكوب العملاق (VLT) عينيه بالفعل بعد ملاحظات ليلية طويلة ، ونام مشغلو التلسكوب وعلماء الفلك ، بينما يستيقظ الفنيون والمهندسون وعلماء الفلك النهاريون ليوم عمل جديد. لن تتوقف الأنشطة في المختبر الأرضي الفلكي الأكثر إنتاجية في العالم. الائتمان: G.Gillet / ESO
أوضح الفلكي أوليفر هايناد في ESO: “كانت لدينا نافذة قصيرة لاكتشاف كويكبنا الخطير”.
ومما زاد الطين بلة ، أنها عبرت جزءًا من السماء[{” attribute=””>Milky Way just behind. Our small, faint, receding asteroid would have to be found against a backdrop of thousands of stars. These would turn out to be some of the trickiest asteroid observations we have ever made”.
Faintest asteroid ever observed
Over the night of May 24, ESO’s VLT took a series of new images. The data arrived and Olivier and Marco began to process them, stacking subsequent observations on top of each other and removing the background stars: it took some time.

ESO’s Very Large Telescope captures 2021 QM1 which for months topped risk lists around the globe. This pivotal sighting ruled out Earth impact in the year 2052. Over the night of May 24, the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope took a series of images of an asteroid that had topped risk lists around the globe for months. These images were some of the trickiest asteroid experts had taken, as the faint asteroid 2021 QM1 receded from view against a very starry backdrop. A series of images were processed, stacked on top of each other and stars were removed, revealing the faintest asteroid observed. Credit: ESA
The result? A positive detection of the faintest asteroid ever observed. With a magnitude of 27 on the scale used by astronomers to describe the brightness of objects in the sky, 2021 QM1 was 250 million times fainter than the faintest stars visible to the naked eye from a dark spot. (In this astronomical scale of visible magnitudes, the brighter an object appears the lower the value of its magnitude, while the brightest objects reach negative values, e.g. the Sun is magnitude -27).
Olivier was certain this small blur was in fact an asteroid, and Marco was certain that given its location, it was our asteroid.
Safe at last?
With these new observations, our risky asteroid’s path was refined, ruling out an impact in 2052, and 2021 QM1 was removed from ESA’s risk list. Another 1,377 remain.

The position of each asteroid at 12:00 CEST on June 13, 2022, is plotted. Each asteroid is a segment representing its motion over 10 days. Inner bodies move faster around the Sun (yellow circle at the center). Blue represents the inner part of the Solar System, where the Near Earth Asteroids, Mars crossers, and terrestrial planets are. The Main Belt, between Mars and Jupiter, is green. The two orange ‘clouds’ correspond to the Trojan asteroids of Jupiter. Credit: © ESA/Gaia/DPAC; CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO, Acknowledgments: P. Tanga (Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur)
More than one million asteroids have been discovered in the Solar System, almost 30 000 of which pass near Earth, with many more expected to be out there. ESA’s Planetary Defence Office, NEOCC and astronomers around the globe are looking up to keep us safe, working together to ensure we know well in advance if an asteroid is discovered on a collision course.
Watch Asteroid Day Live
How worried are the world’s asteroid experts? How did it feel to track humankind’s most risky asteroid? Get the full story in ESA’s 30-minute program counting down to Asteroid Day live on June 30, airing at 10:25 CEST on AsteroidDay.org and on ESA WebTV.

Fallen trees at Tunguska, Imperial Russia, seen in 1929, 15 km from epicenter of the aerial blast site, caused by the explosion of a meteor in 1908. Credit: Photo N. A. Setrukov, 1928
Asteroid Day is the United Nations-sanctioned day of public awareness of the risks of asteroid impacts, held annually on June 30. This year sees its return to Luxembourg for an in-person event following two years of living entirely in the virtual realm. Asteroid experts from ESA, from across Europe and worldwide will converge on the city to take part in a packed four-hour live program of panels and one-on-one interviews.